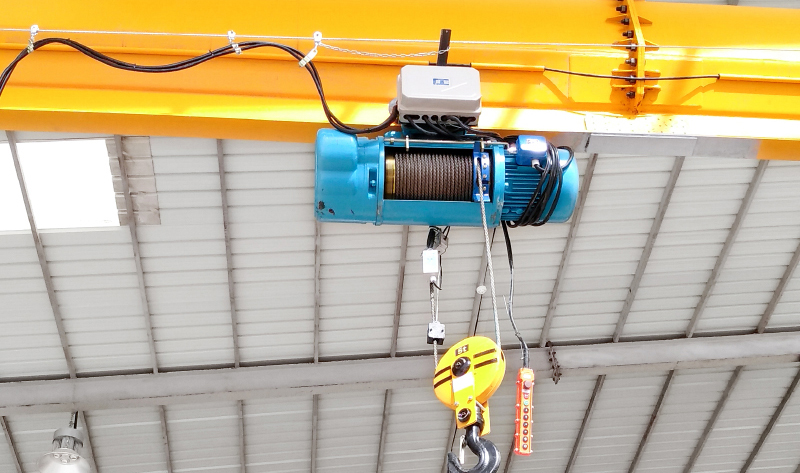
In the world of lifting heavy loads, two stalwarts often stand side-by-side in workshops, 倉庫, 建設現場: the Electric Hoist and the Manual Chain Hoist (often simply called a Chain Hoist or Chain Block). While both serve the fundamental purpose of vertical lifting, their operation, capabilities, and ideal applications differ significantly. Choosing the wrong one can mean inefficiency, operator fatigue, or even inadequate power. Let's break down the key differences.
オンラインチャット
1. Power Source & 手術:
エレクトリックホイスト: Powered by an electric motor. Operation is typically via a push-button pendant control (up/down) or sometimes a radio remote. Requires a reliable electrical power source (single-phase or three-phase, モデルに応じて).
チェーンホイスト: Powered purely by human effort. The operator pulls the hand chain in one direction to lift and the other direction to lower the load. No electricity needed.
2. 持ち上げ速度 & 効率:
エレクトリックホイスト: Significantly faster lifting and lowering speeds. Ideal for repetitive lifting tasks, high-volume operations, or moving loads over greater distances quickly. Boosts productivity dramatically.
チェーンホイスト: Relatively slow lifting speed, entirely dependent on the operator’s strength and stamina. Best suited for occasional lifts, 正確なポジショニング, or lower frequency tasks. Can cause operator fatigue with heavy or frequent use.
3. 持ち上げる容量:
エレクトリックホイスト: Available in a vast range of capacities, from light-duty (例えば。, 250 kg / 0.25 トン) to extremely heavy-duty models (50 tons+). Easily handles larger capacities efficiently.
チェーンホイスト: Also available in a wide range of capacities (例えば。, 500 kg to 20 tons+ common). しかし, the practical capacity is often limited by the operator’s ability to pull the chain effectively, especially near the hoist’s maximum rating. Very high-capacity models require immense effort.
4. コントロール & 精度:
エレクトリックホイスト: Offers good control via variable-speed motors (on many models) for smooth starts/stops and positioning. Easier to operate consistently. しかし, fine “inch” control might require specific features.
チェーンホイスト: Provides excellent tactile feedback and very fine control for precise positioning (例えば。, fitting machinery, aligning components). The operator directly feels the load.
5. インストール & Requirements:
エレクトリックホイスト: Requires proper electrical wiring and often a robust supporting structure (beam, トロリー, ガントリー) due to higher speeds and potential dynamic forces. Installation is generally more complex and requires qualified personnel.
チェーンホイスト: Simpler installation. Primarily needs a suitable anchor point (フック, lug) on a beam or structure. Highly portable – easily moved to different locations.
6. Cost Considerations:
エレクトリックホイスト: Higher initial purchase cost. Requires ongoing electrical costs. Potential for higher maintenance costs due to the motor, ギアボックス, and electrical components.
チェーンホイスト: Lower initial purchase cost. No operating energy costs (beyond operator calories!). Generally lower maintenance costs (歯車, ベアリング, 鎖).
7. Noise & 環境:
エレクトリックホイスト: Generates noise from the motor and gearbox during operation.
チェーンホイスト: Operates silently (aside from chain movement sounds).
8. 安全機能:
Both: Should have essential safety features like load limiters/overload protection and mechanical brakes. エレクトリックホイスト often include additional features like emergency stop buttons, 位相保護, and thermal overload protection for the motor. Chain hoist safety relies heavily on correct operator use and not exceeding capacity.
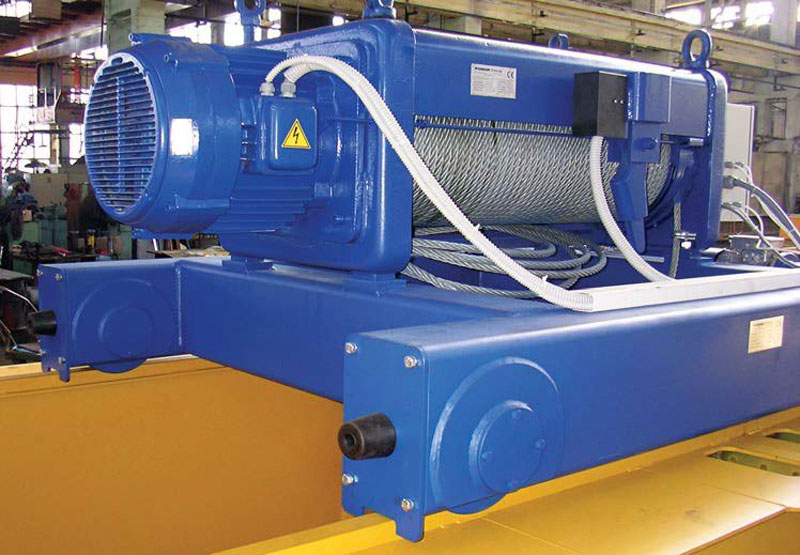

1. High-frequency, repetitive lifting tasks.
2. Lifting heavier loads efficiently.
3. Applications requiring faster lifting/lowering speeds.
4. Situations where operator fatigue needs minimizing.
5. Integration into production lines or automated processes.
6. Lifting over greater heights frequently.
1. Occasional lifting needs.
2. Precise positioning tasks (machinery installation, alignment).
3. Applications where electricity is unavailable, unreliable, or hazardous.
4. Lower capacity lifts where operator effort is manageable.
5. Budget-conscious projects.
6. Situations requiring high portability and quick setup in different locations.
7. Maintenance shops, smaller workshops, field work.
There’s no single “best” hoist. The right choice hinges entirely on your specific needs:
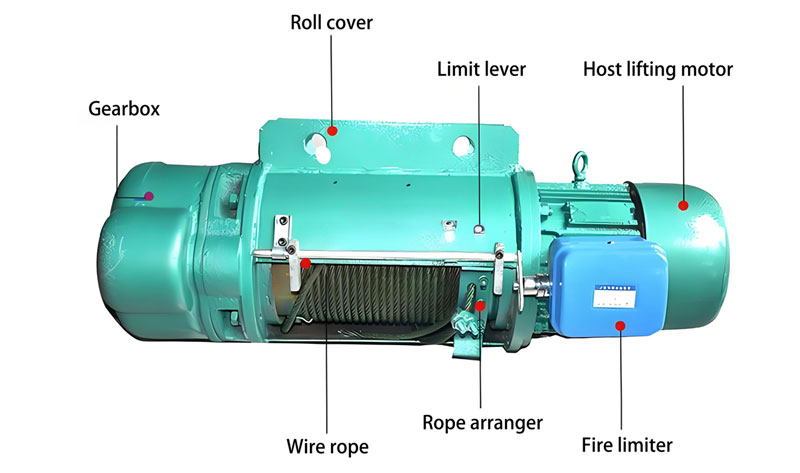
1. Load Weight & Frequency: How heavy, how often?
2. リフトの高さ & Speed Needed: How far, how fast?
3. Power Availability: Reliable electricity on-site?
4. Precision Requirements: Need fine control?
5. Budget: Initial cost vs. long-term operating costs?
6. Portability: Need to move it around frequently?
7. 環境: Dusty, wet, explosive atmosphere? (Requires specific ratings).
By carefully weighing these factors against the strengths and weaknesses of electric and chain hoists, you can confidently select the lifting tool that maximizes safety, 効率, and value for your specific application. 覚えて, sometimes having one of each is the perfect solution for a versatile workspace!

A1: Both come in similar capacity ranges (例えば。, 0.5–20トン以上). しかし, electric hoists handle heavy loads efficiently without operator strain, while manual chain hoists rely on human effort (making very heavy loads impractical for frequent use).
A2: Ideal for:
1. Frequent/repetitive lifting.
2. Heavy loads (1+ トン).
3. Tasks requiring speed or minimal operator fatigue.
4. Production lines or automated settings.
A3: Choose when:
1. Precision positioning is critical (例えば。, machinery alignment).
2. Electricity is unavailable or hazardous.
3. Portability, 低コスト, or occasional use is prioritized.
4. Lighter loads or infrequent lifts.

私たちはあなたのフィードバックを大切にします! あなたの特定のニーズに合わせてサービスを調整できるように、以下のフォームに記入してください.

中国のリフティング機械産業の大手ブランドとして, Woleua Group (weihha) fo……

Weihua Best 電動ホイストがあなたのガレージに最適な理由: パワーハウスパー……

コア強み & オーバーヘッド電気ホイストの重要な機能 1. Robust Construction &a……

従来の電気ホイストでは、フックの高さの間にかなりのヘッドルームが必要です……
