무거운 짐을 들어 올리는 세계에서, 두 명의 충실한 사람이 작업장에서 종종 나란히 서 있습니다., 창고, 그리고 건설현장: 전기 호이스트 및 수동 체인 호이스트 (흔히 체인 호이스트(Chain Hoist) 또는 체인 블록(Chain Block)이라고도 함). 둘 다 수직 리프팅의 기본 목적을 수행하지만, 그들의 운영, 능력, 이상적인 애플리케이션은 크게 다릅니다. 잘못된 선택은 비효율을 의미할 수 있습니다., 운전자 피로, 아니면 힘이 부족하거나. 주요 차이점을 분석해 보겠습니다..
온라인 채팅
1. 전원 & 작업:
전기 호이스트: 전기 모터로 구동. 작동은 일반적으로 푸시 버튼 펜던트 제어를 통해 이루어집니다. (위/아래) 아니면 때로는 라디오 리모콘. 안정적인 전력 공급원이 필요합니다. (단상 또는 삼상, 모델에 따라).
체인 호이스트: 순전히 인간의 노력으로 탄생한. 작업자는 핸드 체인을 한 방향으로 당겨 들어 올리고 다른 방향으로 당겨 하중을 내립니다.. 전기가 필요하지 않습니다.
2. 드는 속도 & 능률:
전기 호이스트: 리프팅 및 하강 속도가 훨씬 빨라졌습니다.. 반복적인 리프팅 작업에 이상적, 대용량 작업, 또는 더 먼 거리에 걸쳐 화물을 빠르게 이동. 생산성을 획기적으로 향상시킵니다..
체인 호이스트: 상대적으로 느린 리프팅 속도, 전적으로 작업자의 힘과 체력에 달려 있습니다.. 가끔 리프트에 가장 적합, 정확한 포지셔닝, 또는 낮은 빈도의 작업. 무겁거나 빈번한 사용으로 인해 작업자의 피로를 유발할 수 있음.
3. 리프팅 용량:
전기 호이스트: 다양한 용량으로 이용 가능, 가벼운 의무에서 (예를 들어, 250 kg / 0.25 톤) 매우 견고한 모델까지 (50 톤+). 더 큰 용량을 효율적으로 쉽게 처리.
체인 호이스트: 다양한 용량으로도 이용 가능 (예를 들어, 500 kg에 20 톤+ 보통). 하지만, 실제 용량은 체인을 효과적으로 당기는 작업자의 능력에 의해 제한되는 경우가 많습니다., 특히 호이스트의 최대 정격 근처. 매우 높은 용량의 모델에는 엄청난 노력이 필요합니다.
4. 제어 & 정도:
전기 호이스트: 가변 속도 모터를 통해 우수한 제어 기능 제공 (많은 모델에서) 원활한 시작/정지 및 위치 결정을 위해. 일관되게 작동하기가 더 쉽습니다.. 하지만, 정밀한 "인치" 제어에는 특정 기능이 필요할 수 있습니다..
체인 호이스트: 정밀한 위치 지정을 위해 뛰어난 촉각 피드백과 매우 미세한 제어 기능을 제공합니다. (예를 들어, 피팅 기계, 구성 요소 정렬). 작업자가 직접적으로 부담을 느끼며.
5. 설치 & 요구사항:
전기 호이스트: 적절한 전기 배선과 견고한 지지 구조가 필요한 경우가 많습니다. (빔, 트롤리, 받침대) 더 빠른 속도와 잠재적인 동적 힘으로 인해. 설치는 일반적으로 더 복잡하며 자격을 갖춘 인력이 필요합니다..
체인 호이스트: 더욱 간단한 설치. 주로 적절한 앵커 포인트가 필요합니다. (훅, 돌기) 빔이나 구조물에. 높은 휴대성 - 다른 위치로 쉽게 이동 가능.
6. 비용 고려 사항:
전기 호이스트: 초기 구매 비용이 높음. 지속적인 전기 비용 필요. 모터로 인해 유지 관리 비용이 높아질 가능성, 변속 장치, 전기 부품.
체인 호이스트: 초기 구매 비용 절감. 운영 에너지 비용 없음 (작업자 칼로리를 넘어서!). 일반적으로 유지 관리 비용이 저렴합니다. (기어, 문장, 체인).
7. 소음 & 환경:
전기 호이스트: 작동 시 모터 및 기어박스에서 소음 발생.
체인 호이스트: 조용히 작동 (체인이 움직이는 소리 외에).
8. 안전 기능:
둘 다: 부하 제한기/과부하 보호 및 기계식 브레이크와 같은 필수 안전 기능을 갖추고 있어야 합니다.. 전기 호이스트 비상 정지 버튼과 같은 추가 기능이 포함되는 경우가 많습니다., 위상 보호, 모터의 열 과부하 보호. 체인 호이스트의 안전은 작업자의 올바른 사용과 용량을 초과하지 않는 것에 크게 좌우됩니다..

1. 고주파, 반복적인 리프팅 작업.
2. 더 무거운 짐을 효율적으로 들어 올리기.
3. 더 빠른 리프팅/하강 속도가 필요한 애플리케이션.
4. 작업자의 피로를 최소화해야 하는 상황.
5. 생산 라인 또는 자동화된 프로세스에 통합.
6. 더 높은 높이로 자주 들어 올리기.
1. 가끔 리프팅이 필요함.
2. 정확한 포지셔닝 작업 (기계 설치, 조정).
3. 전기를 사용할 수 없는 애플리케이션, 신뢰할 수 없는, 아니면 위험하다.
4. 작업자의 노력을 관리할 수 있는 낮은 용량의 리프트.
5. 예산에 민감한 프로젝트.
6. 다양한 위치에서 높은 휴대성과 빠른 설치가 필요한 상황.
7. 정비소, 소규모 작업장, 현장 작업.
단 하나의 "최고" 호이스트는 없습니다. 올바른 선택은 전적으로 귀하의 특정 요구에 달려 있습니다.:
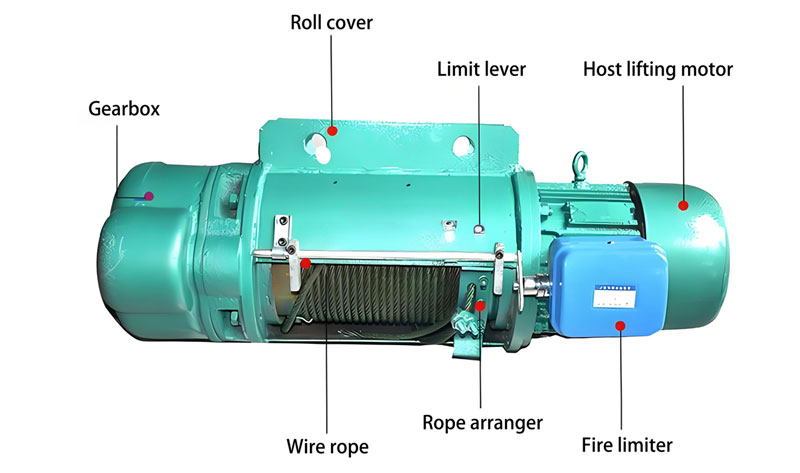
1. 짐 무게 & 빈도: 얼마나 무거워?, 얼마나 자주?
2. 리프트 높이 & 필요한 속도: 얼마나 멀어요, 얼마나 빨리?
3. 전력 가용성: 현장의 안정적인 전기?
4. 정밀도 요구사항: 세밀한 제어가 필요함?
5. 예산: 초기 비용 대비. 장기 운영 비용?
6. 이식성: 자주 옮겨야해요?
7. 환경: 무미 건조한, 젖은, 폭발성 분위기? (특정 등급이 필요합니다).
전기 및 체인 호이스트의 강점과 약점에 대해 이러한 요소를 신중하게 비교함으로써, 안전성을 극대화한 리프팅 도구를 자신있게 선택할 수 있습니다., 능률, 특정 애플리케이션에 대한 가치. 기억하다, 때로는 각각 하나씩 갖는 것이 다용도 작업 공간을 위한 완벽한 솔루션입니다.!

A1: 둘 다 비슷한 용량 범위로 제공됩니다. (예를 들어, 0.5–20톤 이상). 하지만, 전기 호이스트는 작업자의 부담 없이 무거운 하중을 효율적으로 처리합니다., 수동 체인 호이스트는 인간의 노력에 의존하는 반면 (빈번한 사용에는 매우 무거운 하중을 비현실적으로 만듭니다.).
A2: 다음에 이상적입니다.:
1. 자주/반복적으로 들어올리기.
2. 무거운 짐 (1+ 톤).
3. 속도가 필요하거나 작업자의 피로가 최소화되는 작업.
4. 생산 라인 또는 자동화된 설정.
A3: 언제 선택하세요:
1. 정밀한 포지셔닝이 중요합니다 (예를 들어, 기계 정렬).
2. 전기를 사용할 수 없거나 위험함.
3. 이식성, 저렴한 비용, 또는 가끔씩 사용하는 것이 우선시됩니다..
4. 더 가벼운 짐 또는 드물게 들어올리는 경우.

우리는 귀하의 의견을 소중히 여깁니다! 귀하의 특정 요구에 맞게 서비스를 조정할 수 있도록 아래 양식을 작성하십시오..

20 FT 전기 케이블 호이스트 매개 변수 분류 매개 변수 이름 세부 기본 P ……

전통적인 전기 호이스트는 후크의 높이 사이에 상당한 헤드 룸이 필요합니다 ……

창고에서, 공장, 전 세계 조립 라인, 시간은 최고의 화폐이다. 티……

Weihua Electric Hoi를 통해 손쉬운 리프팅과 정밀한 자재 취급을 경험해보세요…
