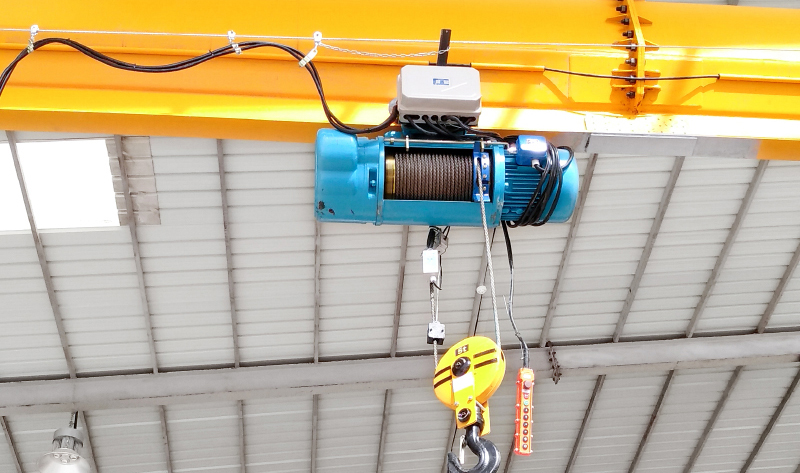
在举升重物的世界里, 车间里经常有两位伟人并肩站立, 仓库, 和建筑工地: 电动葫芦和手动环链葫芦 (通常简称为环链葫芦或环链葫芦). 虽然两者都服务于垂直提升的根本目的, 他们的运作, 能力, 和理想的应用有很大不同. 选择错误可能意味着效率低下, 操作员疲劳, 甚至电量不足. 让我们来分解一下关键的区别.
在线聊天
1. 电源 & 手术:
电葫芦: 由电动机提供动力. 通常通过按钮吊坠控制进行操作 (上/下) 或者有时是无线电遥控器. 需要可靠的电源 (单相或三相, 取决于模型).
环链葫芦: 纯粹由人力提供动力. 操作员向一个方向拉动手链以提升负载,向另一个方向拉动以降低负载. 无需电力.
2. 提升速度 & 效率:
电葫芦: 提升和下降速度显着加快. 重复性提升任务的理想选择, 大批量操作, 或快速移动负载更远的距离. 显着提高生产力.
环链葫芦: 提升速度相对较慢, 完全取决于操作者的体力和耐力. 最适合偶尔升降, 精准定位, 或较低频率的任务. 大量或频繁使用可能导致操作员疲劳.
3. 提升能力:
电葫芦: 具有多种容量可供选择, 从轻型 (例如。, 250 公斤 / 0.25 吨) 至超重型型号 (50 吨+). 轻松高效地处理更大的容量.
环链葫芦: 还具有多种容量可供选择 (例如。, 500 公斤至 20 吨+普通). 然而, 实际能力往往受限于操作者有效拉动链条的能力, 特别是接近葫芦的最大额定值时. 非常高容量的模型需要付出巨大的努力.
4. 控制 & 精确:
电葫芦: 通过变速电机提供良好的控制 (在许多型号上) 用于平稳启动/停止和定位. 更容易持续操作. 然而, 精细的“英寸”控制可能需要特定的功能.
环链葫芦: 提供出色的触觉反馈和非常精细的控制,以实现精确定位 (例如。, 装配机械, 对齐组件). 操作者直接感受到负载.
5. 安装 & 要求:
电葫芦: 需要适当的电线,通常还需要坚固的支撑结构 (光束, 手推车, 龙门架) 由于更高的速度和潜在的动力. 安装通常比较复杂,需要合格的人员.
环链葫芦: 安装更简单. 主要需要一个合适的锚点 (钩, 凸耳) 在梁或结构上. 高度便携——轻松移动到不同地点.
6. 成本考虑:
电葫芦: 初始购买成本较高. 需要持续的电力成本. 电机可能导致更高的维护成本, 变速箱, 和电气元件.
环链葫芦: 较低的初始购买成本. 无运营能源成本 (超出操作员卡路里!). 维护成本普遍较低 (齿轮, 轴承, 链).
7. 噪音 & 环境:
电葫芦: 运行期间电机和变速箱产生噪音.
环链葫芦: 安静运行 (除了链条运动的声音).
8. 安全功能:
两个都: 应具有负载限制器/过载保护和机械制动器等基本安全功能. 电葫芦 通常包括紧急停止按钮等附加功能, 缺相保护, 和电机热过载保护. 环链葫芦的安全在很大程度上取决于操作员的正确使用和不超过容量.
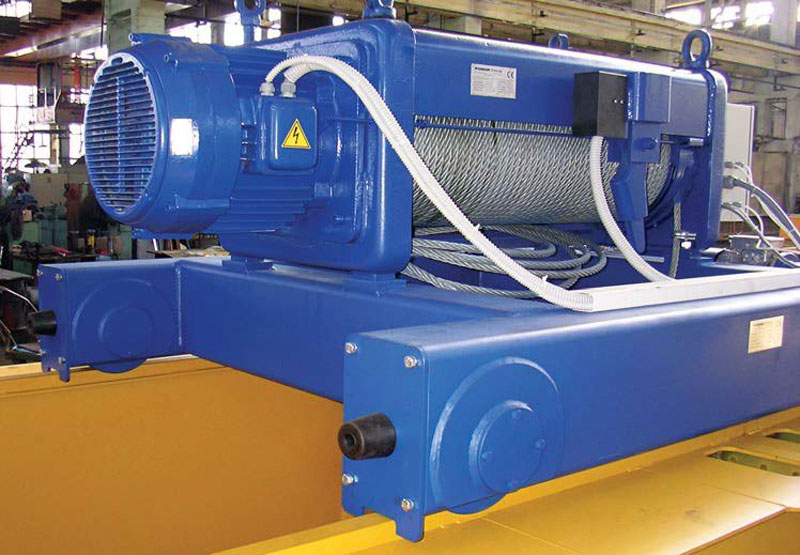

1. 高频, 重复性的起重任务.
2. 有效提升较重的负载.
3. 需要更快提升/降低速度的应用.
4. 需要尽量减少操作员疲劳的情况.
5. 集成到生产线或自动化流程中.
6. 经常举起更高的高度.
1. 偶尔需要起重.
2. 精准定位任务 (机械安装, 结盟).
3. 没有电力的应用, 不可靠的, 或危险的.
4. 电梯运载能力较低,操作员的工作量是可控的.
5. 注重预算的项目.
6. 需要高便携性和在不同地点快速设置的情况.
7. 维修店, 较小的作坊, 实地工作.
没有单一的“最佳”提升机. 正确的选择完全取决于您的具体需求:
1. 负载重量 & 频率: 有多重, 多常?
2. 提升高度 & 需要速度: 多远, 多快?
3. 功率可用性: 现场供电可靠?
4. 精度要求: 需要精细控制?
5. 预算: 初始成本与. 长期运营成本?
6. 可移植性: 需要经常搬动它?
7. 环境: 尘土飞扬, 湿的, 爆炸性环境? (需要特定的评级).
通过仔细权衡这些因素与电动葫芦和环链葫芦的优缺点, 您可以放心地选择安全性最大化的起重工具, 效率, 以及对您的特定应用的价值. 记住, 有时,两者各有一个是多功能工作空间的完美解决方案!

A1: 两者的容量范围相似 (例如。, 0.5–20+吨). 然而, 电动葫芦可有效搬运重物,操作员不会感到紧张, 而手动环链葫芦则依靠人力 (使得非常重的负载对于频繁使用来说不切实际).
A2: 非常适合:
1. 频繁/重复举重.
2. 重负载 (1+ 吨).
3. 需要速度或最小程度操作员疲劳的任务.
4. 生产线或自动化设置.
A3: 选择何时:
1. 精准定位至关重要 (例如。, 机械对准).
2. 电力不可用或存在危险.
3. 可移植性, 低成本, 或优先考虑偶尔使用.
4. 较轻的负载或不频繁的升降机.

我们重视您的反馈! 请填写下面的表格,以便我们可以根据您的特定需求来量身定制服务.

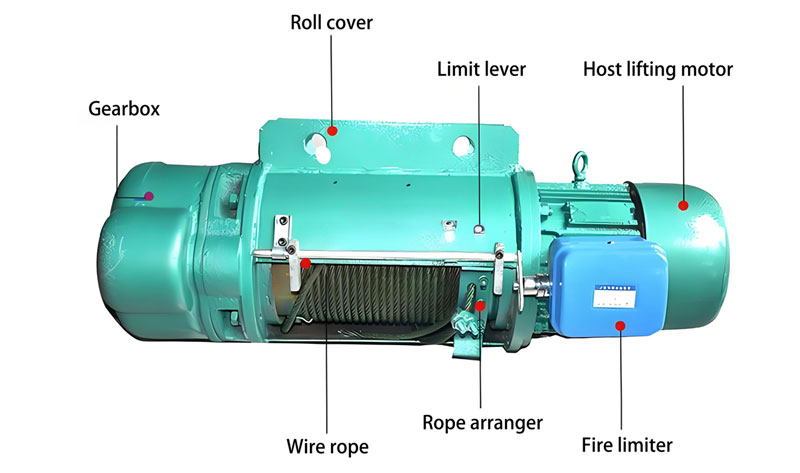
这 5 环链电动葫芦是一种高效、安全的起重设备,专门设计……

2 吨环链电动葫芦核心参数 范围 详细说明 额定功率……

Weihua电动提升的主要特征 1. 高起重能力 & VE……

可变的速度电动芯芯可变频率驱动模块使用Infineon IGB……
